JavaSE-OOP(01)
Java Class and Objects
Class类可以被看成一个蓝图(设计图),在我们创建一个对象之前,我们需要一张设计图来确定它由什么部分构成,有什么功能等。于此同时,我们可以用一张图纸(类)来创造出许多对象,这一点体现了类的复用性。简而言之,Java通过类将复杂问题抽象成一个个对象去解决,所以说是面向对象的Object-orinted。
class ClassName {
// fields
// methods
}main方法
❓我一开始学Java的时候,就让我在一个叫做main的方法里打代码,这个方法是什么,为什么
🙋♂️:
main方法由public,static,void修饰,表明他是可以被外部调用的、静态调用的、同时无返回值。main方法就像python中的if __name__ == __main__一样,它一般被进行测试类的方法和实现
Method Overloading
- 两个或者更多的方法可以拥有同一个名字,如果他们接受不同的参数(实际上,说明
方法名称+参数是区分方法的唯一标识) - 方法的重载可以通过以下方法实现
- 改变参数的数量
- 改变参数的数据类型
- 只改变一个方法的返回类型显然不是方法重载,因为
方法名称+参数才是区分方法的唯一标识
Constructor
在Java中,构造器可以被分为3种
No-Arg Constructor 无参数的构造函数
如果一个构造函数不接受任何参数,那么它是一个无参构造函数
Parameterized Constructor 带参数的构造函数
带参数的构造函数在对象创建,传递对应参数时创建
Default Constructor 默认构造函数
如果我们没有指定构造函数,那么Java会生成默认的构造函数,默认的构造函数会初始化实例的字段
| Type | Default Value |
|---|---|
boolean |
false |
byte |
0 |
short |
0 |
int |
0 |
long |
0L |
char |
\u0000 |
float |
0.0f |
double |
0.0d |
object |
Reference null |
构造器-你需要知道的
重点
- 构造器在你进行对应的初始化操作时执行
- 构造器的名称要和类的名称相同
- 如果不指定构造函数,Java会自动生成默认构造函数进行初始化操作
- 构造函数不能由
static和abstract修饰- 构造函数可以重载但是不能重写
class Main { String language; // constructor with no parameter Main() { this.language = "Java"; } // constructor with a single parameter Main(String language) { this.language = language; } public void getName() { System.out.println("Programming Langauage: " + this.language); } public static void main(String[] args) { // call constructor with no parameter Main obj1 = new Main(); // call constructor with a single parameter Main obj2 = new Main("Python"); obj1.getName(); obj2.getName(); } }
String
字符串,顾名思义就是字符的序列
String Operations
Length
获取字符串长度:greet.length()
Join two Strings
拼接字符串:first.concat(second)
Compare two Strings
比较两个字符串:first.equlas(second)
❓对于String来说 == 和 equals()方法有什么区别
==用于确认两个引用对象是不是相同的equals()用于确认内容是否相同
| Methods | Description |
|---|---|
| substring() | returns the substring of the string |
| replace() | replaces the specified old character with the specified new character |
| charAt() | returns the character present in the specified location |
| getBytes() | converts the string to an array of bytes |
| indexOf() | returns the position of the specified character in the string |
| compareTo() | compares two strings in the dictionary order |
| trim() | removes any leading and trailing whitespaces |
| format() | returns a formatted string |
| split() | breaks the string into an array of strings |
| toLowerCase() | converts the string to lowercase |
| toUpperCase() | converts the string to uppercase |
| valueOf() | returns the string representation of the specified argument |
| toCharArray() | converts the string to a char array |
Java Strings are Immutable
// add another string "World"
// to the previous tring example
example = example.concat(" World");这段代码实际上是开辟了一个新的空间给example,并不是在原来的example上进行的
JVM通过string pool来维护内存中的strings。当我们通过字面量创建字符串时,它会检查string pool
如果当前字符串已经存在:将这个新的变量指向已存在的那个字符串
不存在:创建一个新的字符串
然而,如果你通过new关键字来创建字符串,因为在创建时你不一定要进行初始化,所以它总是重新开辟一个新的空间来存储这个字符串
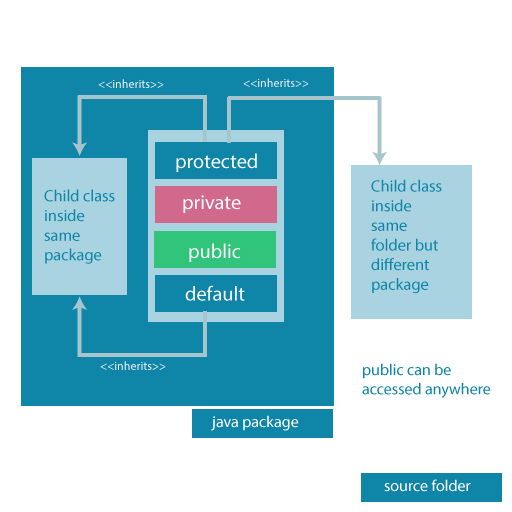
Access Modifier
访问修饰符用于指定改类、方法、字段等对于外界或者自己内部的其他成员是否可以访问。
| Modifier | Description |
|---|---|
| Default | declarations are visible only within the package (package private) 包内可访问 |
| Private | declarations are visible within the class only 类内可访问 |
| Protected | declarations are visible within the package or all subclasses 包于子类内可访问 |
| Public | declarations are visible everywhere 都可访问 |
⚠️:我们在Java中不会定义一个
private类或者接口,因为它们无法被访问。当然在嵌套结构里,你可以定义为private(内部类等)
this Keyword
在Java中,this关键字被用于在method或者constructor中引用当前对象
class Main {
int instVar;
Main(int instVar){
this.instVar = instVar;
System.out.println("this reference = " + this);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main obj = new Main(8);
System.out.println("object reference = " + obj);
}
}下面将介绍this的使用场景
构造函数中区分同名变量
class Main { int age; Main(int age){ this.age = age; } public static void main(String[] args) { Main obj = new Main(8); System.out.println("obj.age = " + obj.age); } }Getter and Setter
class Main { String name; // setter method void setName( String name ) { this.name = name; } // getter method String getName(){ return this.name; } public static void main( String[] args ) { Main obj = new Main(); // calling the setter and the getter method obj.setName("Toshiba"); System.out.println("obj.name: "+obj.getName()); } }用于构造器的重载
在一个构造函数中调用另一个构造函数,需要通过
this来调用class Complex { private int a, b; // constructor with 2 parameters private Complex( int i, int j ){ this.a = i; this.b = j; } // constructor with single parameter private Complex(int i){ // invokes the constructor with 2 parameters this(i, i); } // constructor with no parameter private Complex(){ // invokes the constructor with single parameter this(0); } @Override public String toString(){ return this.a + " + " + this.b + "i"; } public static void main( String[] args ) { // creating object of Complex class // calls the constructor with 2 parameters Complex c1 = new Complex(2, 3); // calls the constructor with a single parameter Complex c2 = new Complex(3); // calls the constructor with no parameters Complex c3 = new Complex(); // print objects System.out.println(c1); System.out.println(c2); System.out.println(c3); } }用于传递参数
final Keyword
当一个实体(变量、方法或者类)被定义为final,它就能只能初始化,不可再赋值
final 变量不能再次初始化
通常我们用Uppercase来声明一个常量
final int AGE = 32;final 方法不能重写,会编译错误
final 类不能被继承,会编译错误
本文由 Frank采用 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0)许可
Java — 2021年4月19日
Made with ❤ and at Hangzhou.