JavaSE-Flow Control&Array
for loop vs for-each loop
普通的for loop可以获得数组下标,再获取对应的值
for-each loop方便与直接获取值,但是得不到下标
Java的循环可以有标号,用于label一个循环,以跳出多重循环
OUT: // 作为循环可以直接跳出 for (i=0; i <10; i++) { for (j=0; j <10; j++) { if (j == 5) { break OUT; } } }当然除了
break你也可以使用continue
while vs do-while vs for
While, Do while, for:选择哪一个?
- 固定次数:使用 for
- 必须执行一次:使用do while
- 其他情况:使用while
Arrays
Declare
Java数组的声明由两个部分组成:数据类型以及数组名称
dataType[] arrayName;- dataType可以是
原始数据类型 primitive也可以为类 - 数组名称规则与变量名规则相同
但是一个数组能放多少元素呢?
🙋好问题!我们可以通过以下两种方法给数组分配空间
// 1. 先声明再分配
double[] data;
data = new Double[10];
// 2. 声明+分配
double[] data = new Double[10];Initialize
数组的初始化有两种方法:
在声明的同时初始化
int[] age = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5};注意,这种
{12, 4, 5, 2, 5}初始化方法只能在声明的同时初始化,因为它在初始化的同时也分配了数组的空间。如果你先分配了空间,那么你得到会是一个数组地址,因此对其进行初始化是不被允许的。int[] age = new int[5]; // age = {12, 4, 5, 2, 5} - 不被允许的对数组空间一一赋值
// declare an array int[] age = new int[5]; // initialize array age[0] = 12; age[1] = 4; age[2] = 5; ..
Loop with Array
Java中数组有一个length属性,代表数组的长度,因此可以用于遍历
for (int i = 0; i<age.length; i++)
{
System.out.println(age[i]);
}Multidimensional Arrays
int[][] a = new int[3][4];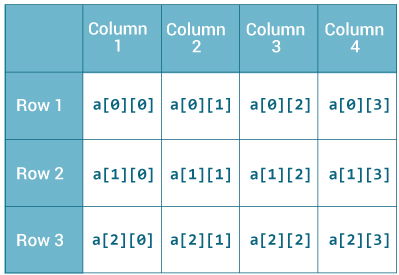
Initialize 2d array
int[][] a = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6, 9},
{7},
};同理的,你可以遍历赋值,但是此时a.length == 3,每一个元素为一行,以此类推
Copy Array
浅拷贝 shallow copy
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int [] positiveNumbers = numbers; // copying arrays
// change value of first array
numbers[0] = -1;
// printing the second array
for (int number: positiveNumbers) {
System.out.print(number + ", ");
}
}
}深拷贝 deep copy
import java.util.Arrays;
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] source = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int [] destination = new int[6];
// iterate and copy elements from source to destination
for (int i = 0; i < source.length; ++i) {
destination[i] = source[i];
}
// converting array to string
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(destination));
}
}
浅拷贝vs深拷贝:浅拷贝指向的是同一块存储空间,所以是同一个对象
深拷贝是重新复制出新的一个对象,和原对象一起是两个对象
使用Array.arraycopy()
import java.util.Arrays;
Arrays.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,Object dest, int destPos, int length)- src - source array you want to copy
- srcPos - starting position (index) in the source array
- dest - destination array where elements will be copied from the source
- destPos - starting position (index) in the destination array
- length - number of elements to copy
Array.copyOfRange()
copyOfRange()方法与arraycopy()的不同之处在于,它返回的数组切片的一个复制,并没有目标数组地址来指向。我们可以直接生成一个数组。
// To use toString() and copyOfRange() method
import java.util.Arrays;
class ArraysCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] source = {2, 3, 12, 4, 12, -2};
// copying entire source array to destination
int[] destination1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(source, 0, source.length);
System.out.println("destination1 = " + Arrays.toString(destination1));
// copying from index 2 to 5 (5 is not included)
int[] destination2 = Arrays.copyOfRange(source, 2, 5);
System.out.println("destination2 = " + Arrays.toString(destination2));
}
}本文由 Frank采用 署名 4.0 国际 (CC BY 4.0)许可
Java — 2021年4月16日
本文总阅读量次
Java
Next posts
JavaSE-OOP(01)
Previous posts
JavaSE-Introduction
View / Make Comments
Made with ❤ and at Hangzhou.
本站总访问量次